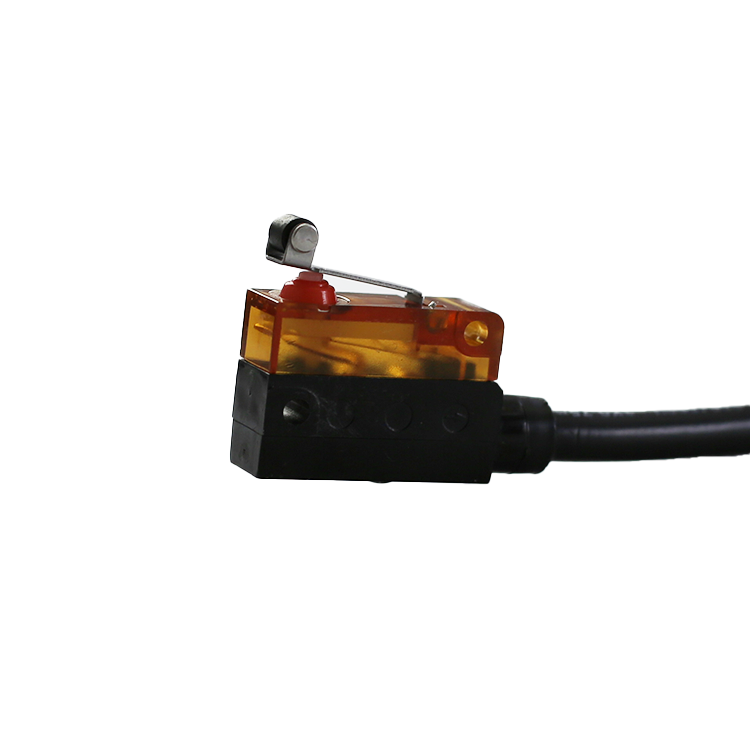

What are the common failures and treatments that microswitches may encounter in rail transit operations?
Microswitches play an integral role in rail transit systems. These small, albeit unobtrusive, devices are a critical part of keeping trains running safely and smoothly. However, as with any high-precision device, microswitches can experience a variety of malfunctions over long periods of operation. The following is a discussion of seven common failures and their treatment methods that microswitches may encounter in rail transit operations:
read more>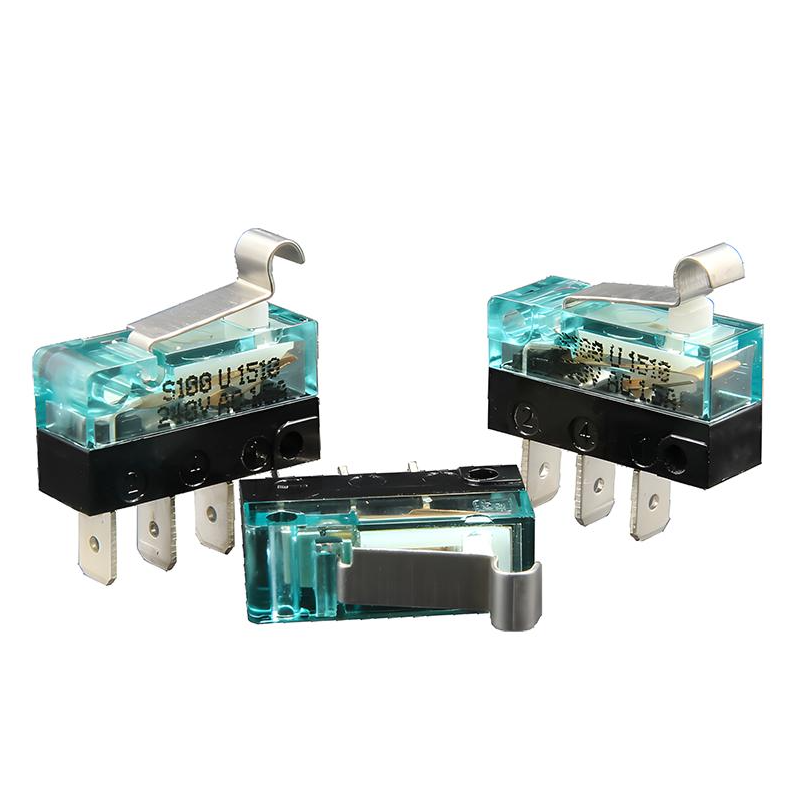
How to consider durability and reliability when buying microswitches?
When purchasing microswitches, it is critical to consider their durability and reliability. To gain insight into how to ensure that the microswitch you select will meet your specific needs in terms of longevity and reliability, consider the following dimensions
read more>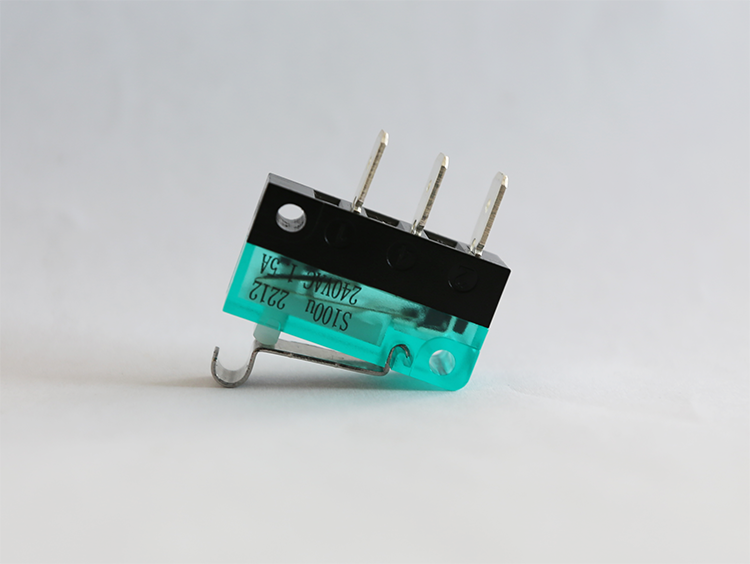
What do I need to pay attention to for the installation and maintenance of rail transit microswitches?
In the vast field of rail transportation, the tacit cooperation of countless precision components is indispensable behind every safe trip. Microswitch, this small and inconspicuous components, but in every journey of the train plays an irreplaceable role. They are like tiny guardians, silently ensuring the smooth operation of the train and the safety of passengers.
read more>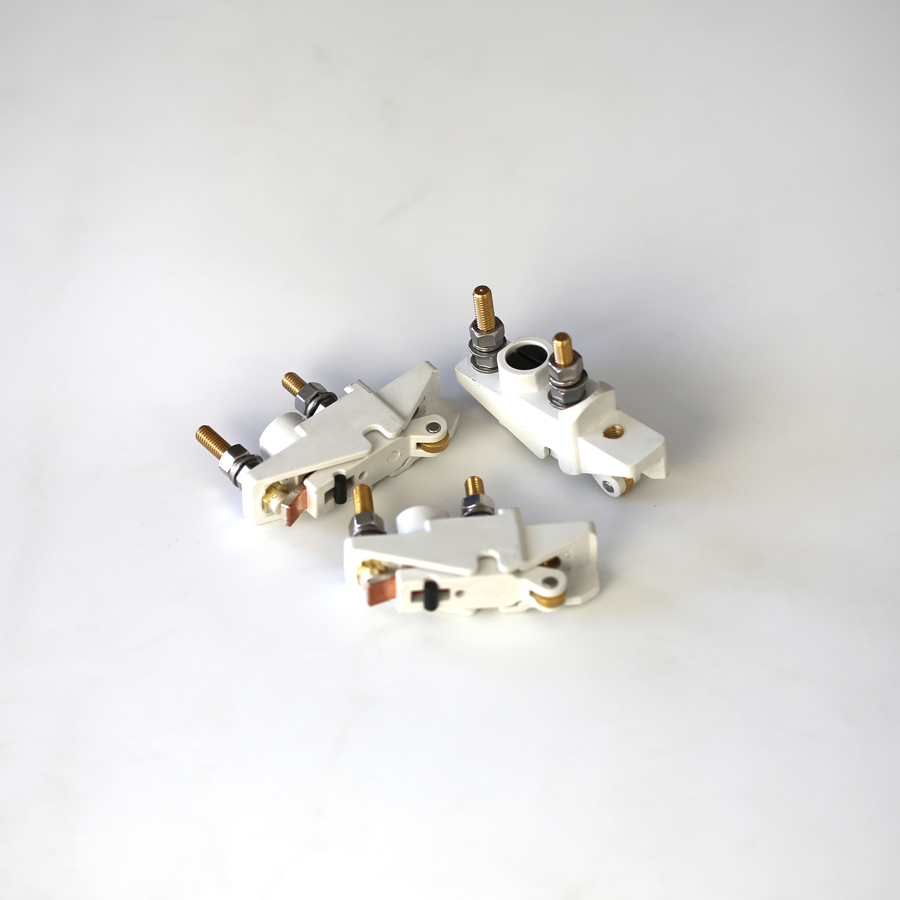
Auxiliary switches: the guardians of power system security
In every corner of the electric power system, whether it is a bustling urban high-rise, or a remote mountain village hut, the stable supply of electricity can not be separated from a series of precision equipment to protect. Among them, the auxiliary switch may be a little-known role, but it bears a significant responsibility that can not be ignored. Today, let us explore this silent hero - auxiliary switch, revealing its role and importance in the power system.
read more>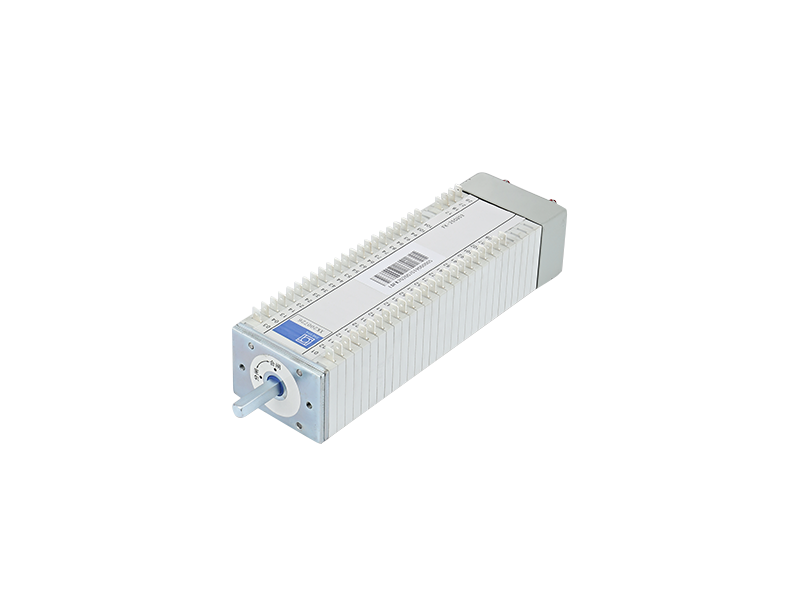
Special requirements for the working environment of microswitches in rail transportation
In the vast field of rail transportation, the tacit cooperation of countless precision components is indispensable behind every safe trip. Microswitches, a small and inconspicuous component, play an irreplaceable role in every journey of the train. They are like tiny guardians, silently ensuring the smooth operation of the train and the safety of passengers.
read more>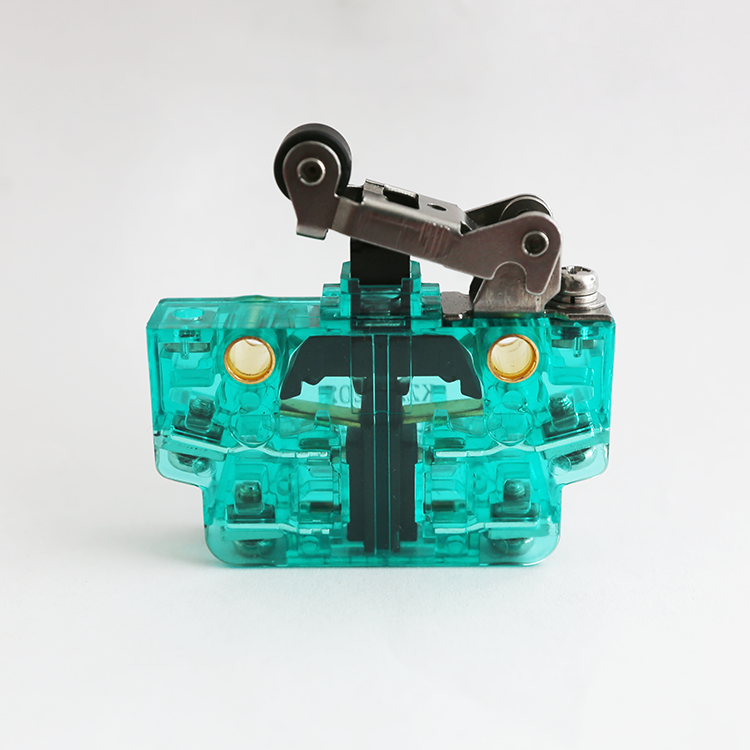
How to choose the right microswitch model?
Size matters when selecting a microswitch. Switch size is directly related to its characteristics, including current range, travel, and operating force. For example, one of the smallest microswitches on the market today measures 0.50 inches x 0.236 inches x 0.197 inches (LxWxH). While this tiny switch is suitable for use in compact circuit breakers for detecting circuit status, it is typically capable of interrupting only 0.1 to 3 amps (A) and has a short stroke. Applications requiring higher currents usually require larger switches. For example, a microswitch used to detect liquid level in a tank application would need to be able to provide a large stroke and withstand high currents. Often in level switch applications, the switch is used to directly drive a pump and carry a high current. This requires a large microswitch rated at 20A or 25A at 125VAC or 250VAC. Tip: The smaller the switch size, the less travel and current it can break.
read more>
