

The heart of precision craftsmanship: stamping die selection for automotive parts processing
Release time:2024-05-23
In the giant wheel of modern industry, automobile manufacturing is undoubtedly one of the most central parts. The birth of each car is the result of the convergence of countless precision parts. And in the production of these parts, stamping die plays a vital role. They are not only the tools of the manufacturing process, but also the cornerstone to ensure the accuracy and quality of the parts. So, what type of stamping dies are suitable for automotive parts processing? Let's explore this topic full of technology and wisdom.
First, we must recognize the diversity and complexity of automotive parts. From lightweight body coverings to sturdy structural frames, each part has its own unique shape, size and performance requirements. Therefore, choosing the right type of stamping die is like customizing a “suit” for each part.
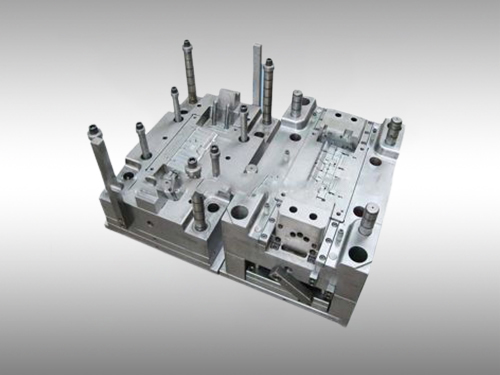
For large coverings, such as doors, roofs and hoods, continuous or progressive dies are usually used. These molds are characterized by the ability to complete multiple processes, such as cutting, forming and punching, in succession, which greatly improves productivity. Their design is usually complex and requires precise calculation of material flow and pressure distribution to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the finished product.
For structural parts, such as vehicle frames, suspension systems and seat supports, more robust composite or transfer molds are required. These molds are able to withstand high intensity pressures to ensure the shape and strength of the part. Their design focuses on the plastic deformation of the material and the durability of the mold to ensure the stability and reliability of the part over a long period of time.
In addition, with the automotive industry's increasing demand for lightweight and environmental protection, new materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloys and composites are being used more and more widely. These materials put forward higher requirements for stamping molds. For example, high-strength steel requires molds with higher wear resistance and impact resistance, while aluminum alloys require molds with good thermal stability and low coefficient of friction.
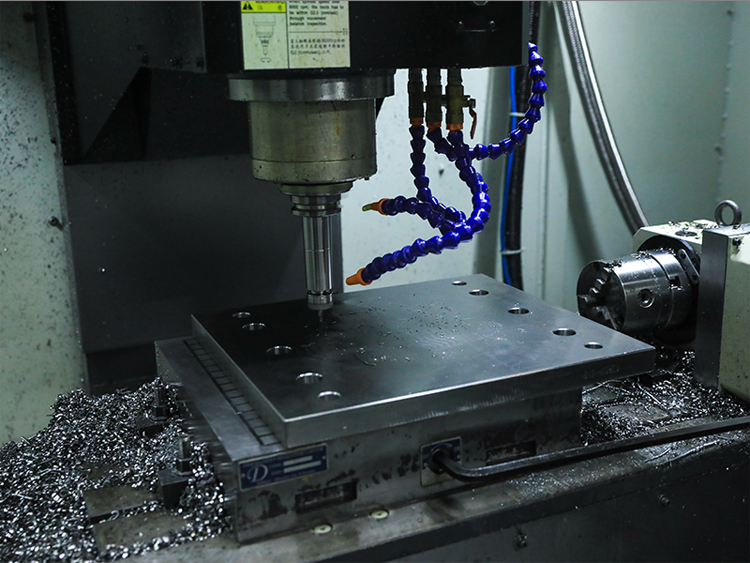

In terms of mold material selection, high-quality tool steel is a common material that provides good hardness and toughness. For more demanding conditions, tungsten steel and cemented carbide are better choices, which offer higher wear resistance and temperature stability.
Finally, we can't ignore the intelligence and automation of mold design. With the development of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology, mold design has been able to achieve a high degree of accuracy and efficiency. Through simulation analysis, engineers can predict and optimize the performance of the mold before production, thus reducing the cost of trial and error and increasing production speed.

In conclusion, the selection of stamping dies for automotive parts processing is an esoteric art, which requires comprehensive consideration of the characteristics of the part, the material requirements and the efficiency of production. Every right choice is a silent commitment to automotive safety and performance. In this field full of challenges and opportunities, every engineer engaged in mold design and manufacturing is an artist guarding the heart of precision craftsmanship in the automotive industry.
First, we must recognize the diversity and complexity of automotive parts. From lightweight body coverings to sturdy structural frames, each part has its own unique shape, size and performance requirements. Therefore, choosing the right type of stamping die is like customizing a “suit” for each part.

For large coverings, such as doors, roofs and hoods, continuous or progressive dies are usually used. These molds are characterized by the ability to complete multiple processes, such as cutting, forming and punching, in succession, which greatly improves productivity. Their design is usually complex and requires precise calculation of material flow and pressure distribution to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the finished product.
For structural parts, such as vehicle frames, suspension systems and seat supports, more robust composite or transfer molds are required. These molds are able to withstand high intensity pressures to ensure the shape and strength of the part. Their design focuses on the plastic deformation of the material and the durability of the mold to ensure the stability and reliability of the part over a long period of time.
In addition, with the automotive industry's increasing demand for lightweight and environmental protection, new materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloys and composites are being used more and more widely. These materials put forward higher requirements for stamping molds. For example, high-strength steel requires molds with higher wear resistance and impact resistance, while aluminum alloys require molds with good thermal stability and low coefficient of friction.

In terms of mold material selection, high-quality tool steel is a common material that provides good hardness and toughness. For more demanding conditions, tungsten steel and cemented carbide are better choices, which offer higher wear resistance and temperature stability.
Finally, we can't ignore the intelligence and automation of mold design. With the development of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology, mold design has been able to achieve a high degree of accuracy and efficiency. Through simulation analysis, engineers can predict and optimize the performance of the mold before production, thus reducing the cost of trial and error and increasing production speed.

In conclusion, the selection of stamping dies for automotive parts processing is an esoteric art, which requires comprehensive consideration of the characteristics of the part, the material requirements and the efficiency of production. Every right choice is a silent commitment to automotive safety and performance. In this field full of challenges and opportunities, every engineer engaged in mold design and manufacturing is an artist guarding the heart of precision craftsmanship in the automotive industry.
